The main drawback of JFET is that its gate must be reversed biased for proper operation of the device. This means that it can only have a negative gate operation for an n - channel and a positive gate operation for a p - channel. This means that one can only decrease the width of the channel from its zero bias and this type of operation is referred to as DEPLETION MODE.
Thus a JFET can only be operated in depletion mode.
However, there is an FET (Field Effect Transistor) that can be operated to enhance the width of the channel resulting o enhancement, such an FET is called MOSFET and the mode is known as ENHANCEMENT MODE.
Merits of MOSFET (Metallic Oxide Semiconductor FET) over JFET are:
1. Low Cost of Production
2. High Input Impedance
There are two basic types of MOSFET which are:
1. D-MOSFET: This MOSFET can operate in both enhancement and depletion modes.
2. E-MOSFET: This MOSFET can operate in only enhancement mode.
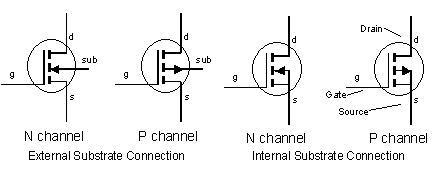
A MOSFET like a JFET has 3 basic terminals which are the gate, source and drain. The substrate is connected the source internally.
Since the gate is insulated from the channel one can apply either positive or negative voltage to the gate. Therefore making it possible for D-MOSFET to be operated in both enhancement and depletion modes.
It is worthy to note that the E-MOSFET has no channel between the source and drain unlike the D-MOSFET. The substrate extends completely to the SiO2 layer so that no channel exists. The E-MOSFET requires a proper gate voltage to form a channel.
Note that since gate is insulated from the channel, the MOSFET is sometimes called INSULATED GATE FET.
Take for example an n - channel D-MOSFET, the gate, SiO2 layer and the channel form a capacitor where one plate is the gate, the dielectric is the metal oxide semiconductor (SiO2 layer) and the other plate is the channel.
When gate voltage is changed, the electric field of the capacitor changes which in turn changes the resistance of the n - channel D-MOSFET.
As said earlier, the gate is insulated from the channel thus, one can apply either a negative or positive voltage to the gate.
The application of a negative voltage to the gate results to a depletion mode while the application of a positive voltage to the gate results to an enhancement mode.
Depletion Mode
Since the gate is negative, it means that electrons are on the gate. These electrons repel the free electrons in the n - channel, leaving a layer of positive ions in a part of the channel. Through this, one (operator) has depleted the n - channel of some of its free electrons. Therefore, lesser number of free electrons are made available for current conduction through the n - channel. This is similar to increase in the resistance of the channel. The greater the negative voltage on the gate, the lesser the current from source to drain. Thus by changing the negative voltage on the gate, one (operator) can vary the resistance of the n - channel and hence the current from source to drain.
Enhancement Mode
Since the gate is positive, it induces negative charges in the n - channel. These negative charges are free electrons drawn to the channel. Because these free electrons are added to those electrons already in the channel, the total number of free electrons in the channel is increased. Therefore, the greater the positive voltage applied to the gate the lesser the resistance at the channel and the more current moving from the source to drain.
Possible Biasing of D-MOSFET are:
1. Gate Bias
2. Self Bias
3. Voltage Divider Bias
4. Zero Bias
Possible Biasing of E-MOSFET are:
1. Drain Feedback Bias
2. Voltage Divider Bias

No comments:
Post a Comment